Recently, an interesting paper was accepted to CVPR 2024, Depth Anything: Unleashing the Power of Large-Scale Unlabeled Data. The authors made publicly available their pre-trained models in three sizes: Depth-Anything-Small, Depth-Anything-Base, and Depth-Anything-Large.
I wanted to have an idea of how fast these models can run on a CPU these days. Since I am interested in real-time operation, I started with the smallest model to get an idea of how well it performed and how fast it can run the inference in my laptop:
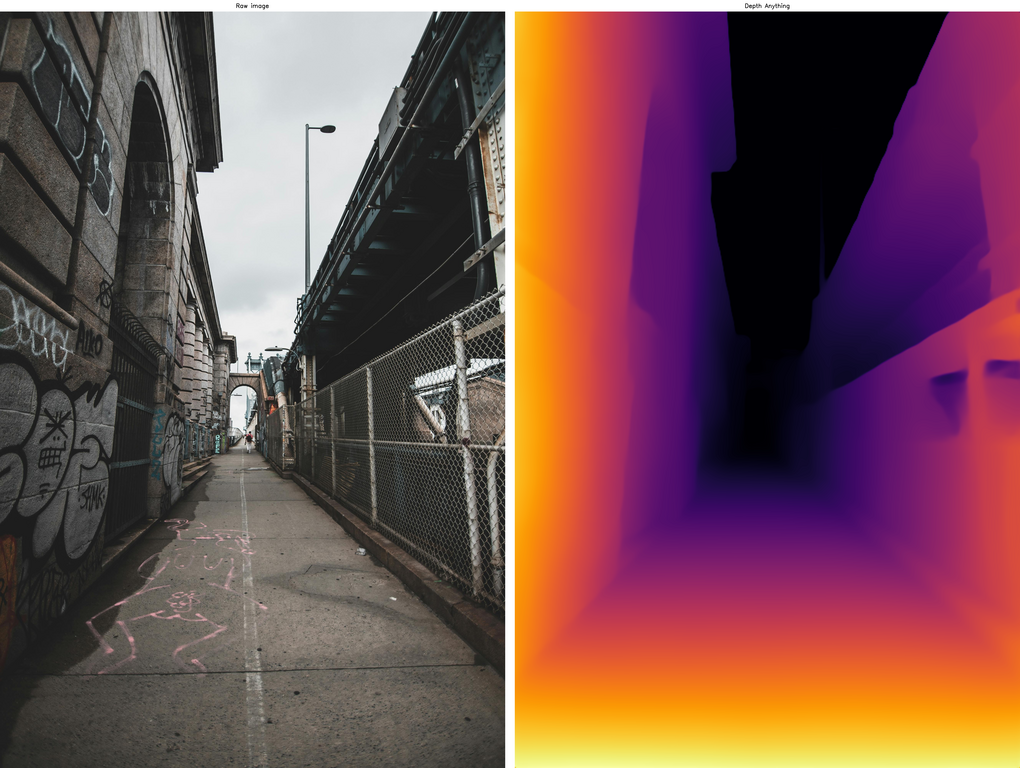
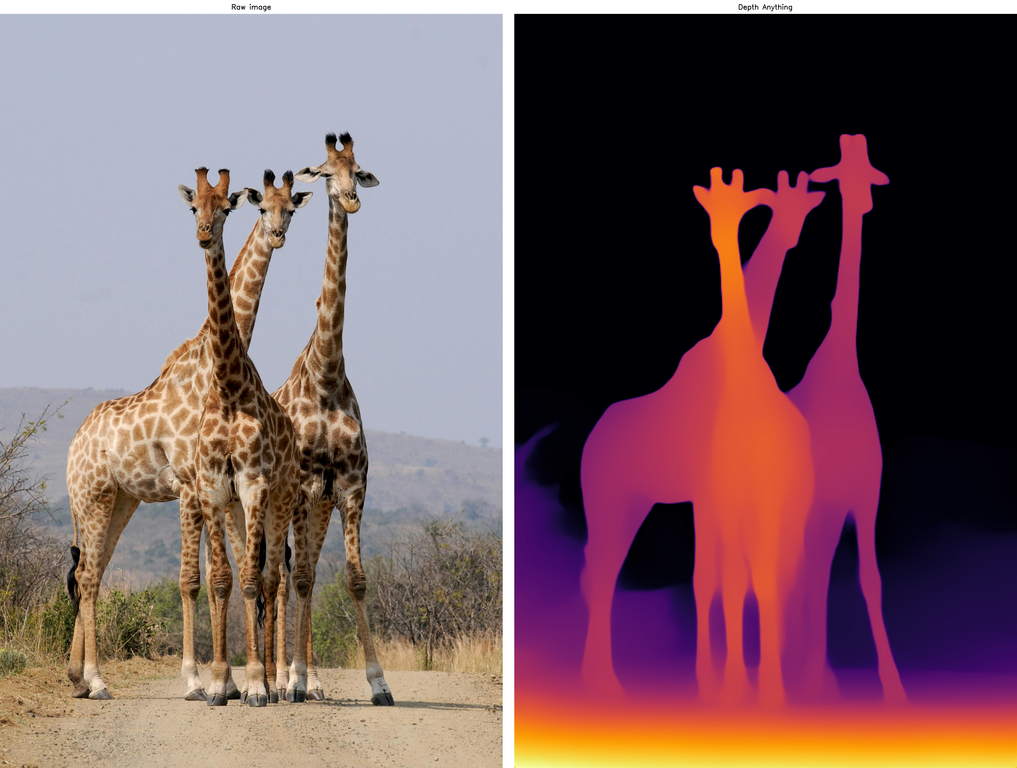



You can see that the smallest model still performs relatively well. In terms of inference time, it took on average 1.02 seconds per image on my CPU, and the size of this PyTorch model, depth_anything_vits14.pth, is 95MB. It’s fast and small, but not really ideal for real-time applications. Let’s see if we can do better.
OpenVINO uses their own Intermediate Representation format, IR, which is designed to be optimised for inference. Furthermore, you can then generate a quantised model from the already OpenVINO optimised model, getting even better inference times and a smaller model.
Here is a table with the different results on my machine:
| Model Name | Inference speed (FPS) | Model Size (MB) |
| depth_anything_vits14.pth (Original PyTorch model) | ~1 | 95 |
| depth_anything_vits14.(bin+xml) (OpenVINO IR) | 7.65 | 47.11 |
| depth_anything_vits14_int8.(bin+xml) (IR Quantised) | 9.74 | 24.27 |
You can clearly see that there is a massive increase in performance when you use the quantised OpenVINO IR model compared to the original PyTorch model. This allows real time operation on a laptop. And for reference, here is the output of the quantised model:
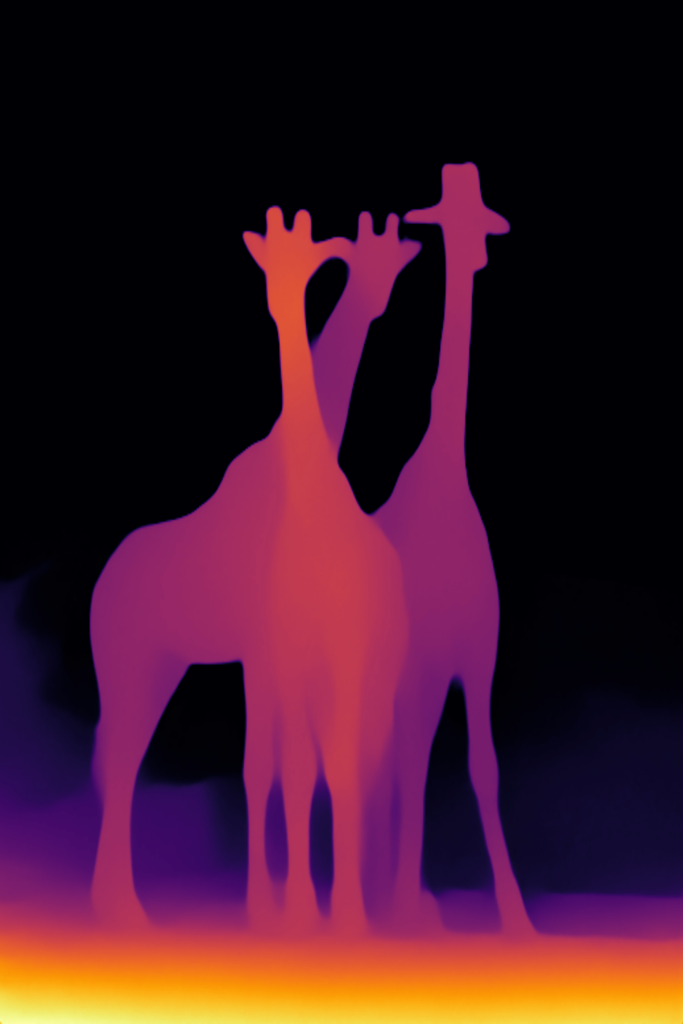

The output is still reasonably good, with the nice bonus that it can be used in real time, plus the file size is about one quarter of the original. All thanks to OpenVINO’s great ability to optimise the inference pipeline!